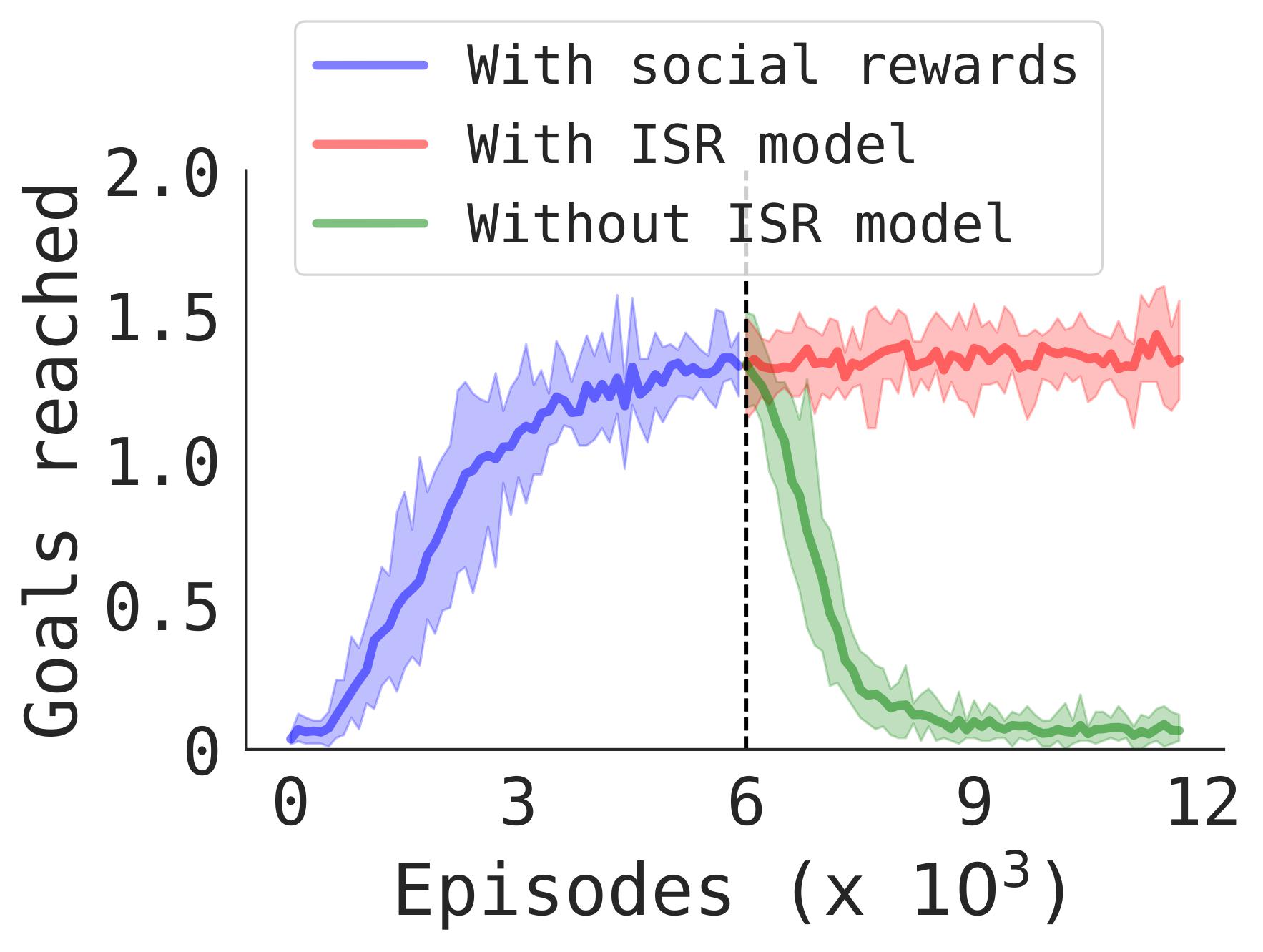
Results

@inproceedings{rong2024value,
title={Value Internalization: Learning and Generalizing from Social Reward},
author={Rong, Frieda and Kleiman-Weiner, Max},
booktitle={Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society},
volume={46},
year={2024}
}